
Below is a step by step example of a standard Wordpress site install with GitHub. This walkthrough does not use all the available parameters provided by the Wordpress plugin, but you can see more available parameters in the Probo Wordpress Plugin documentation.
You can find this Probo.CI example repository here.
You will need:
utf8mb4_unicode_520_ci. See notes below in Prepare your Database.Step 1: Sign into the Probo app and authenticate GitHub.
Go to the Probo app and click on the Login to GitHub button. Once you get to GitHub, click ‘Authenticate application’.
Step 2: Sync your Github Repos.
Your Github repositiories will be synced automatically. You can always click the ‘Sync Repos’ button at the top right corner if you need to manually update your dashboard. Click on the button next to each repo that you want to use with Probo CI.
You will need to import your project’s database within the Probo.CI App, or use the Probo Uploader, a CLI tool. You will first import your database, then you will declare the database file in a .probo.yaml file. We will use the Wordpress plugin to prepare the Wordpress install, import the database, and flush caches. (Cache all the things!)
Step 3: Prepare the Database
Export your existing MySQL database and ensure your database COLLATION is set to utf8mb4_unicode_ci or utf8_unicode_ci in the wordpress.sql file. There is currently an issue importing a DB with utf8mb4_unicode_520_ci COLLATION on our current docker images available for builds. Find and replace utf8mb4_unicode_520_ci with utf8mb4_unicode_ci in your exported wordpress.sql file if you receive the following error in your build:
ERROR 1273 (HY000) at line 25: Unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_unicode_520_ci'
Step 4: Compress your database.
If you wish to compress your database you’ll need to use gzip. Other compressed file types like zip won’t work.
gzip wordpress.sql
Step 5: Install the Probo Uploader on your machine with npm. (Optional)
You will need Node.js for the Probo.CI Uploader. Install node.js and npm if you don’t already have them.
sudo npm install -g probo-uploader
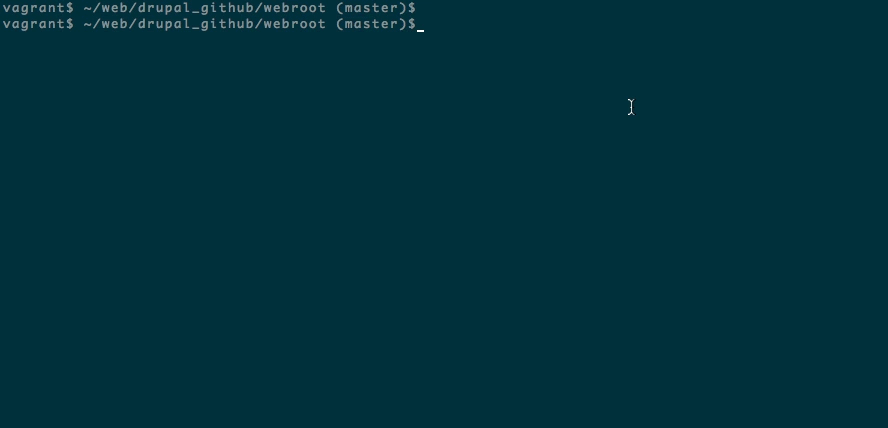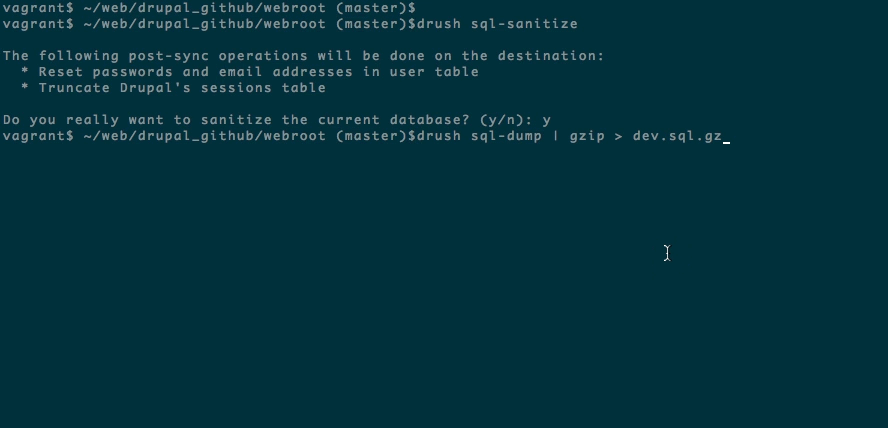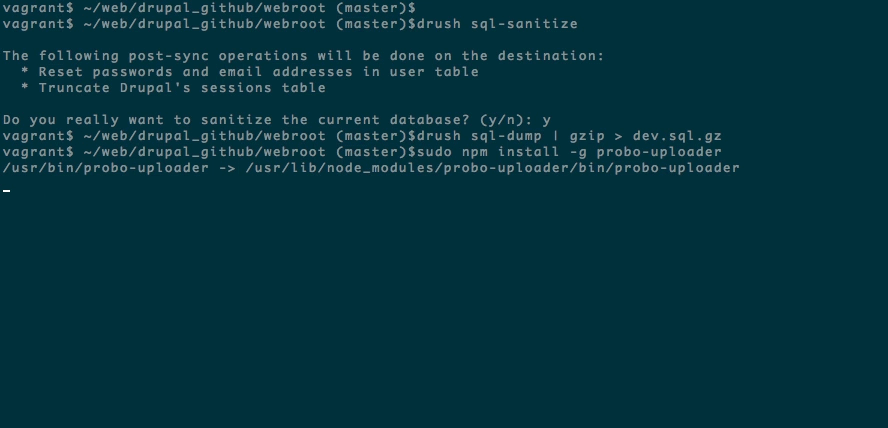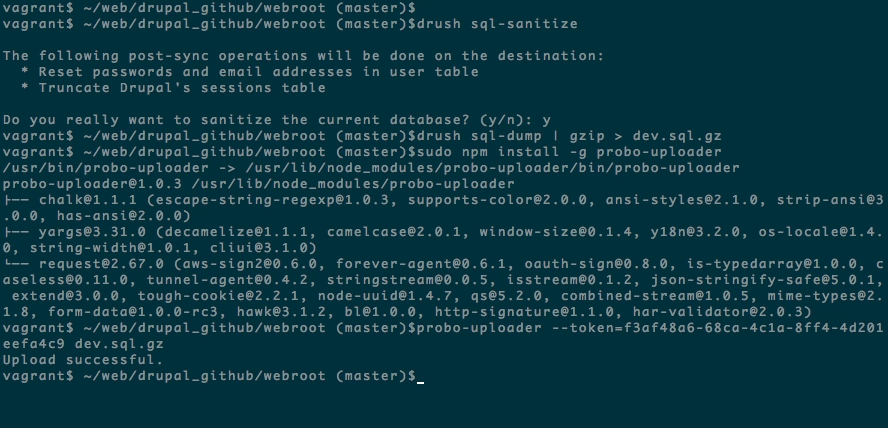
Step 6: Upload your database to the Probo.CI app.
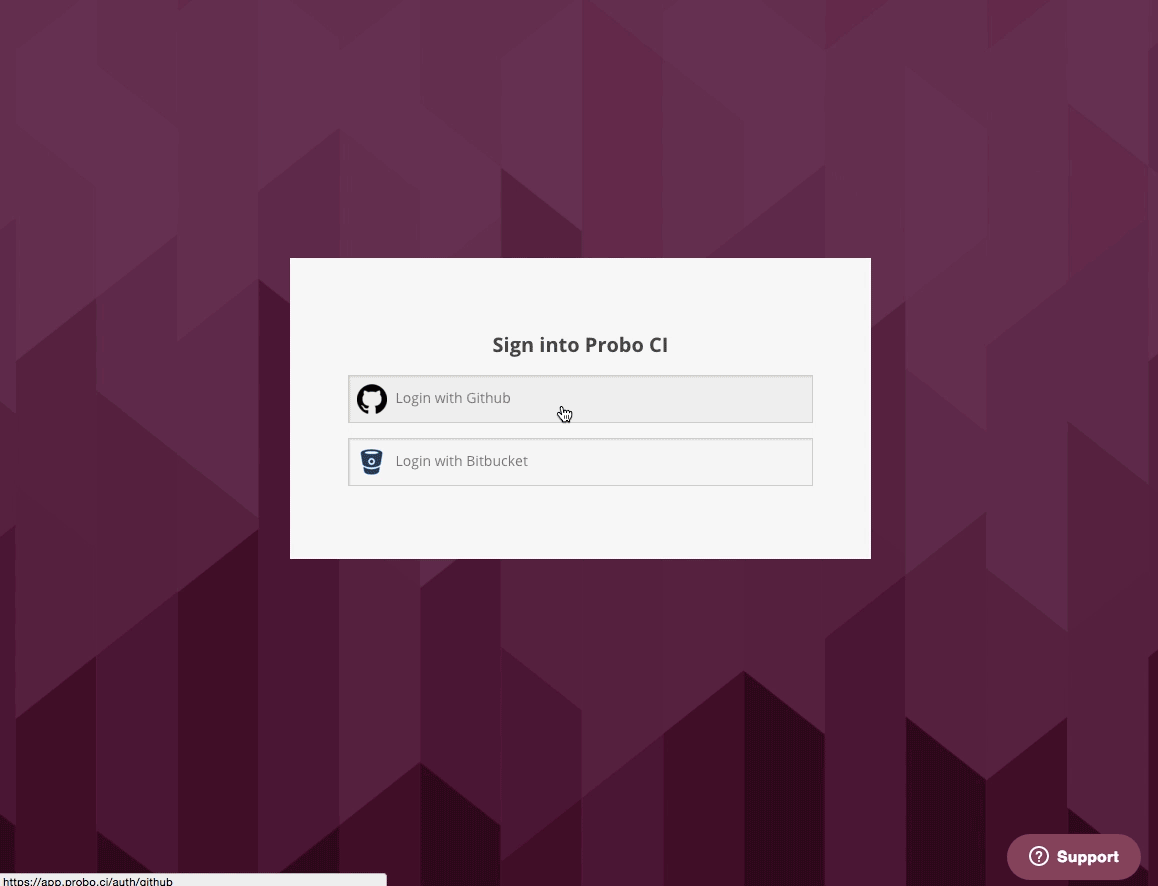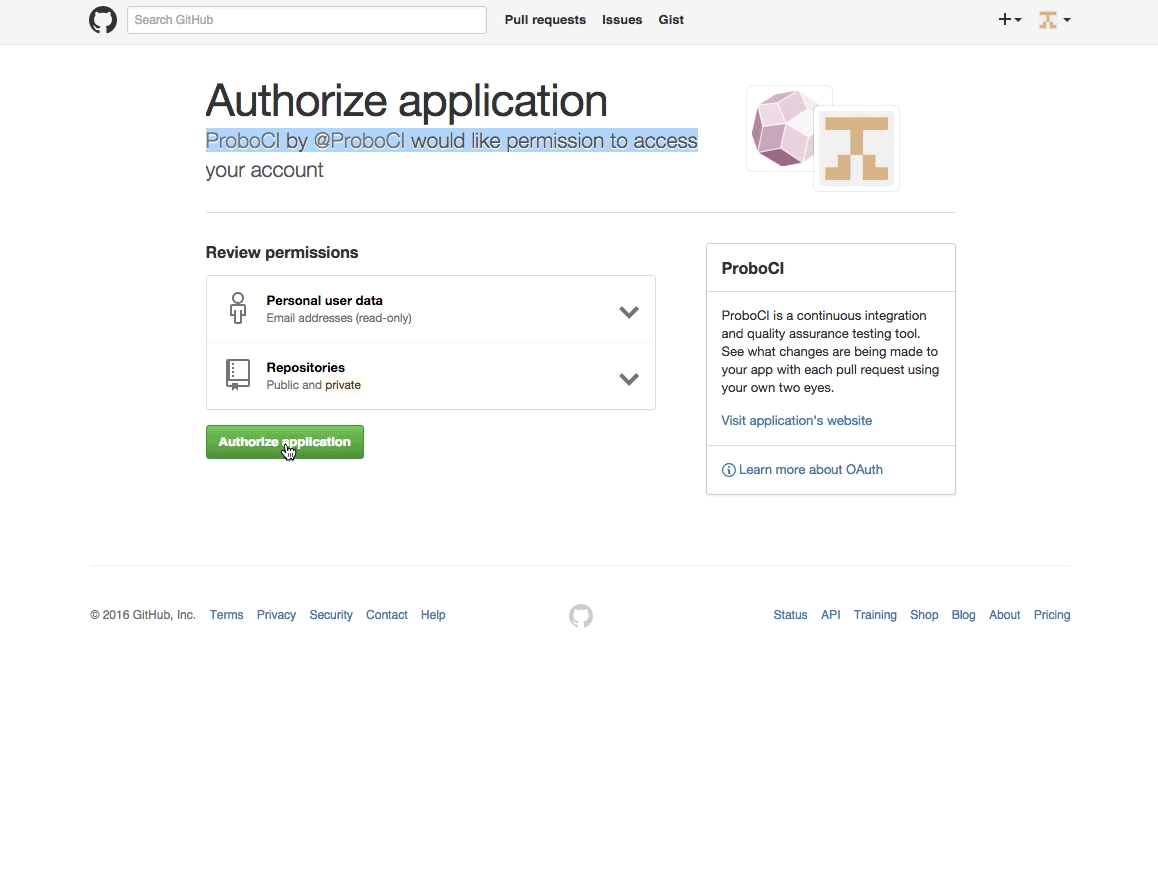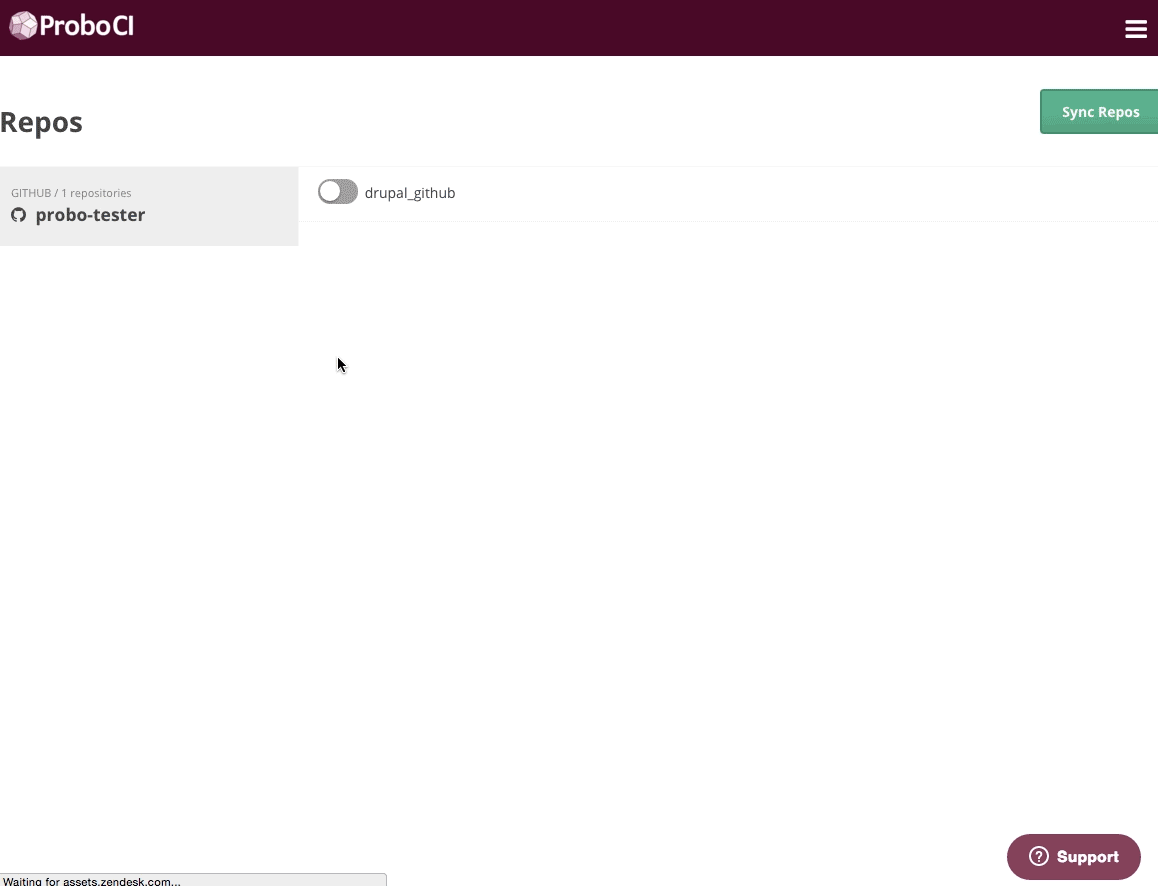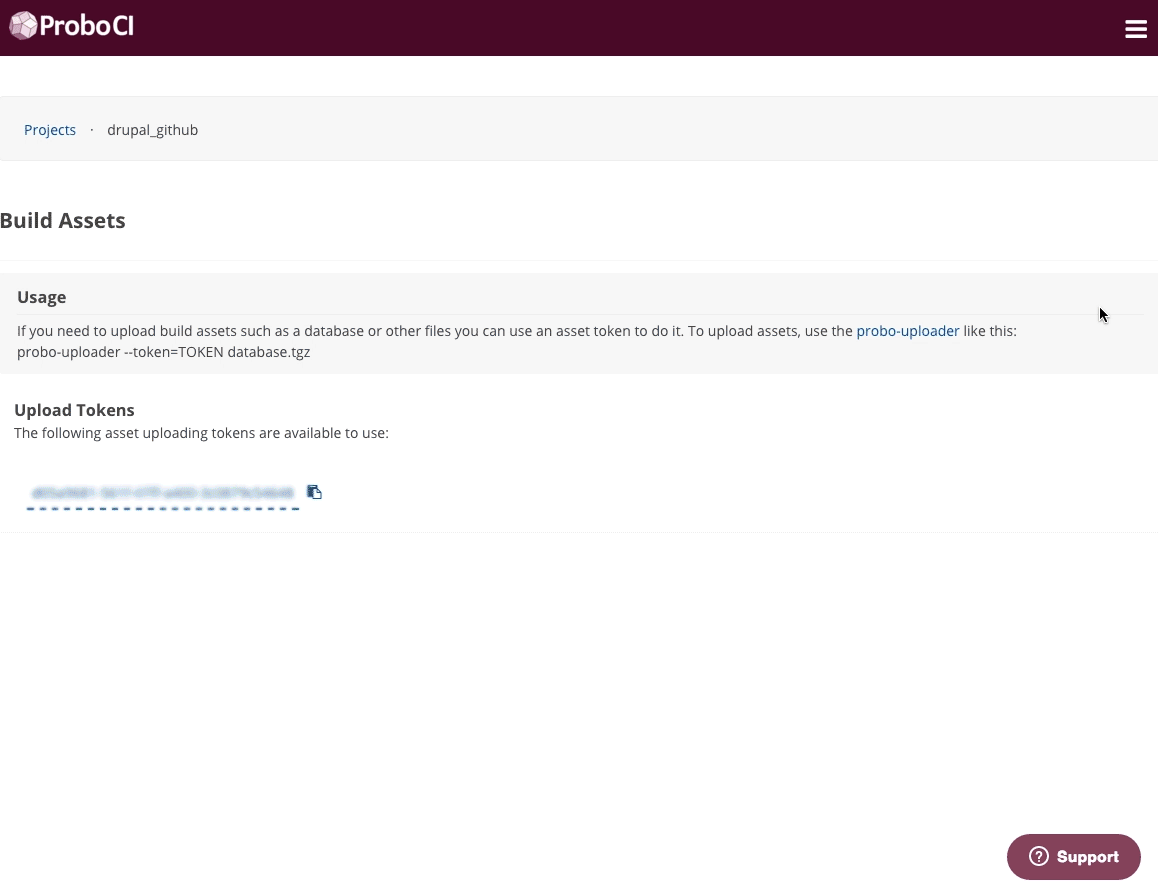
Probo users can now upload database assets and other file assets directly from within the Probo.CI app on the Build Assets tab within their project.
Each repository also has it’s own Upload Token that can be used to upload file assets through the command line. You can find your project’s Upload Token on the Upload Tokens tab within the Probo project.
probo-uploader --token=[your-token] wordpress.sql.gz
The real magic of Probo CI is automating pull requests to create test environments for you. In order to do that, you will need to add a few things to your project.
Step 7: Create a new branch.
cd into your project and create a new branch.
git checkout -b probo-build
Step 8: Create your .probo.yaml file.
You will need a .probo.yaml file in the root of your directory. You can task Probo CI to run any number of build steps. Each step is a runnable plugin, and will get a status update sent to hosted repository for the commit. * Remember that indentation and spacing is important for yaml files.
vim .probo.yaml
Step 9: Declare your assets and build your steps.
Tell Probo.CI what database you are going to use for your Probo.CI builds. Add in your parameters as steps. You can read more in the docs about different parameter options.
assets:
- wordpress.sql.gz
steps:
- name: Site setup
plugin: WordPressApp
database: 'wordpress.sql.gz'
databaseName: 'wordpress'
databaseGzipped: true
subDirectory: 'code'
devDomain: 'http://example.com'
devHome: 'http://example.com/'
flushCaches: true
Note: The wp-cli version we have currently on our docker images is old. Add a step before the Site setup step to update wp-cli if you receive the following error in your “Site setup” build step:
Fatal error: Call to undefined function apply_filters() in /src/wp-includes/load.php on line 316
Update wp-cli in your .probo.yaml steps.
```yaml
assets:
- wordpress.sql.gz
steps:
- name: Update wp-cli.
plugin: Script
script:
- wp cli update --allow-root --yes
- name: Site setup
plugin: WordPressApp
database: 'wordpress.sql.gz'
databaseName: 'wordpress'
databaseGzipped: true
subDirectory: 'code'
devDomain: 'http://example.com'
devHome: 'http://example.com/'
flushCaches: true
```
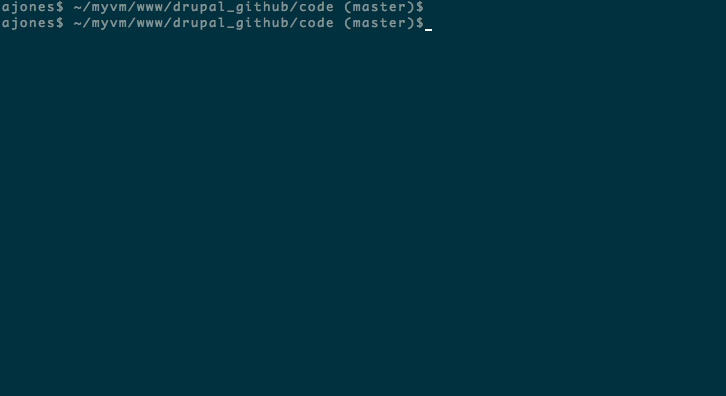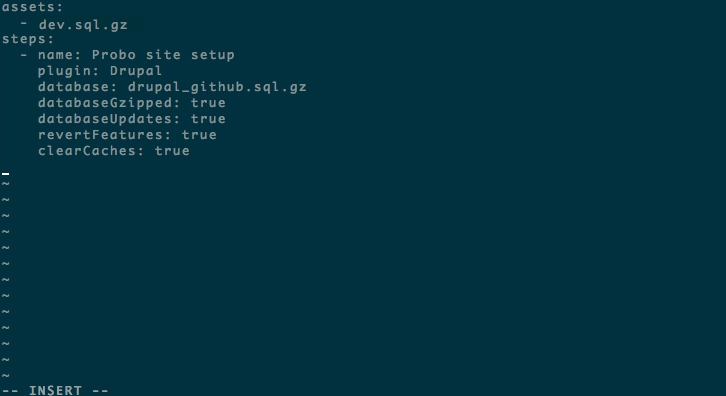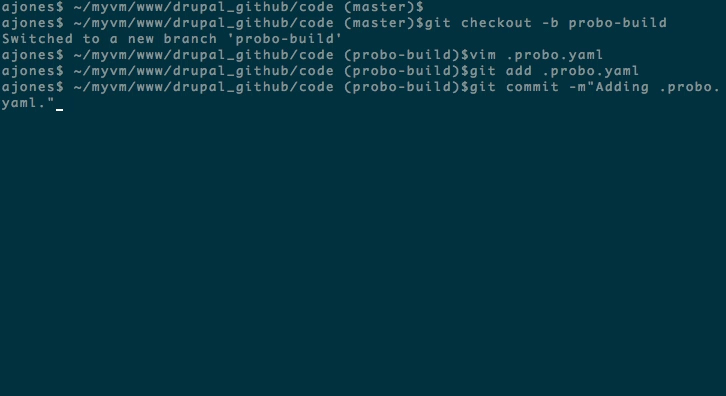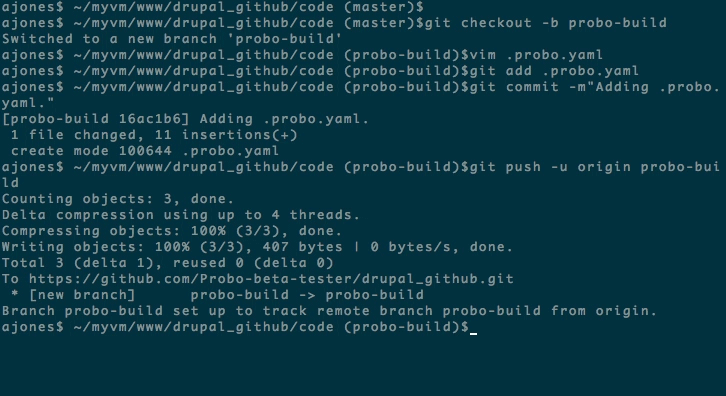
Step 10: In your new branch probo-build, add and commit your files to your remote origin.
git add .probo.yaml
git commit -m "Adding .probo.yaml."
git push -u origin probo-build
Step 11: Go to your GitHub account. You will see your new branch inside your project. https://github.com/Probo-Demos/probo-example-wordpress
Step 12: Create a pull request.
Click ‘New Pull Request’.
Step 13: Bask in the glory of Probo.CI.
In GitHub you will see the Probo.CI build steps. You can now click on any of the details links and it will direct you back to the Probo.CI dashboard.
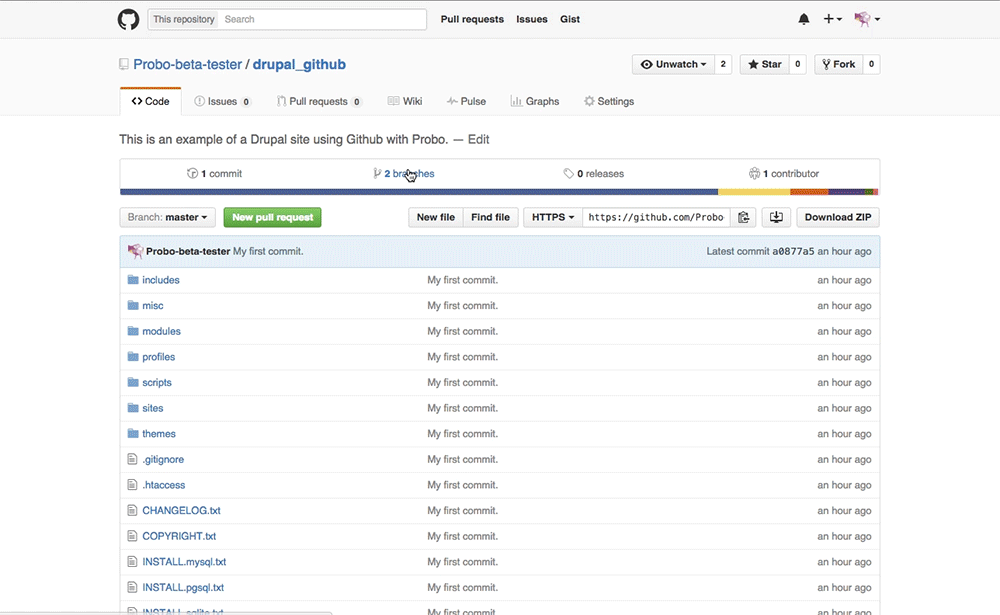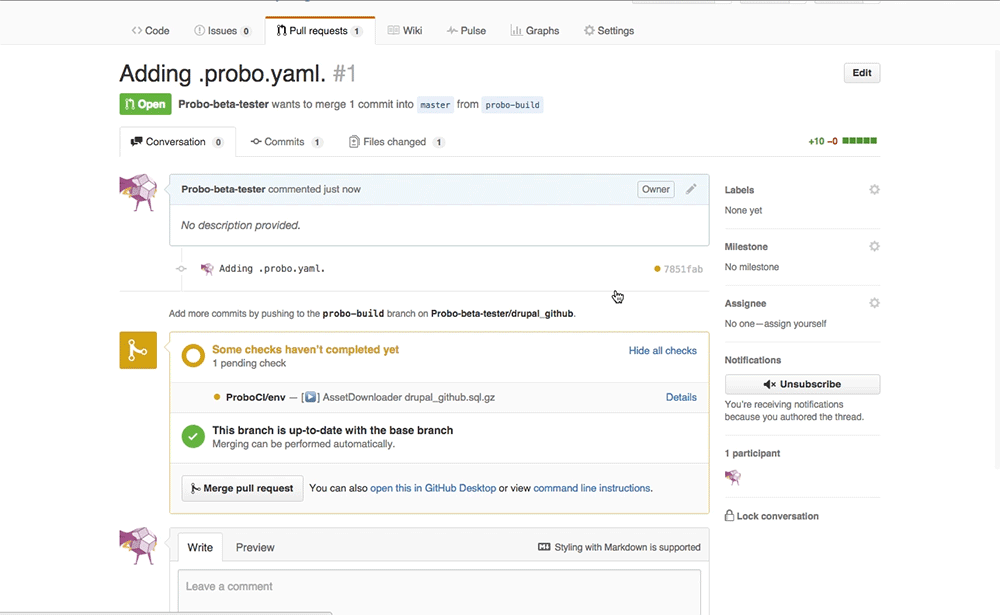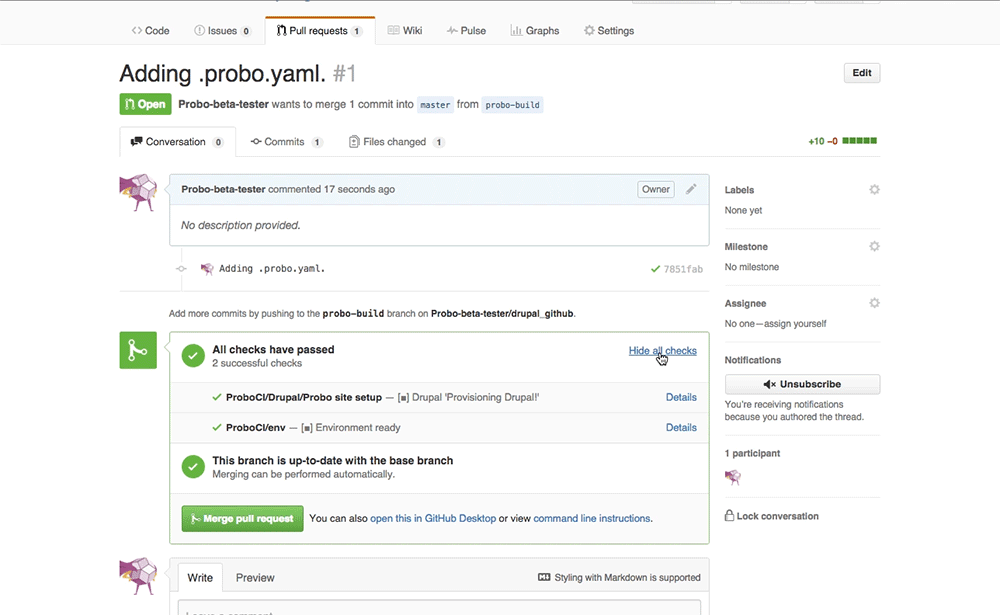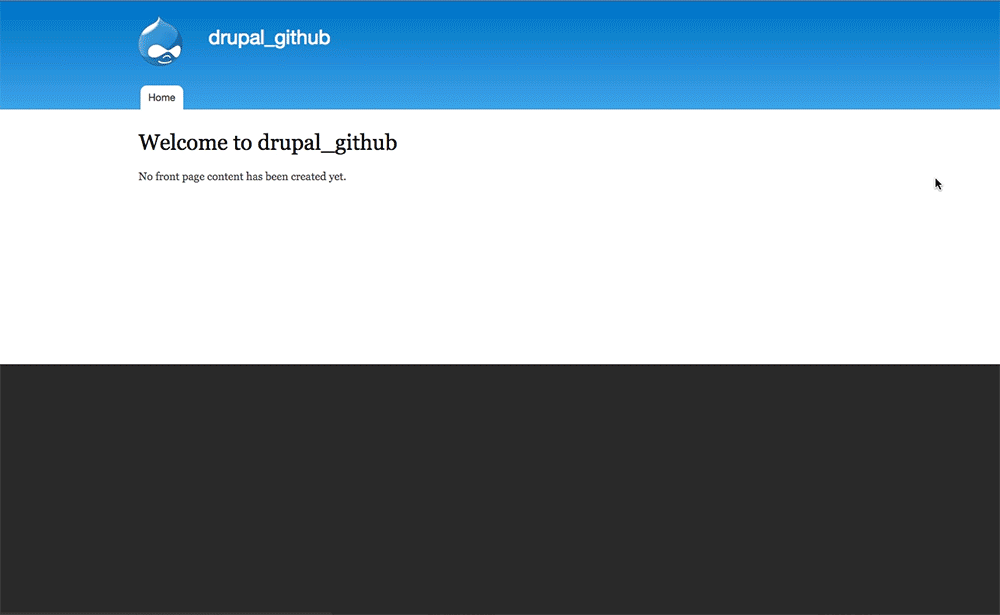
Step 14: See your Probo.CI build.
In your Probo.CI dashboard, click on ‘View build’ and your site will open in a new tab. This Probo.build link uses the database defined in your .probo.yaml file and the code from your pull request.
Step 15: Share your Probo.build link with clients, managers, even your parents.
Note: It might take a few seconds for your Probo.CI environment to build. Wait until all checks have passed before following your Probo.build link.

Get a free trial with our starter plan or look over some of our more advanced plans and choose the best solution for your company or organization!
GET STARTED FREE